Over a period of less than two weeks, since it was officially declared a pandemic by WHO, COVID-19 has disrupted lives and economies around the globe. According to a briefing issued by the United Nations Department of Economic and Social Affairs, the COVID-19 pandemic will likely shrink the global GDP by almost one percent in 2020. Countries have taken unprecedented and drastic measures to contain the spread of the virus by closing towns, cities, and national borders, disrupting not only the big corporations but also millions of SMEs around the world.
With the aim of providing members with the opportunity to share and learn from each other’s experiences, starting in March 2020, the SME Finance Forum has been hosting an hour-long virtual roundtable series for members on the impacts of the COVID-19 crisis. Each meeting features speakers, who describe their institution’s mitigation actions. So far, five sessions were organized where we were able to capture information, experiences, and learnings from the wealth of knowledge brought by peers and colleagues to these sessions. In this blog, we share five key lessons.
Lesson 1: Illiquidity is as dangerous as insolvency:
• Lockdown measures represent a huge squeeze on cash flow, SMEs need capital injections to get through the crisis.
• But, SMEs typically have less than 27 days of cash on hand, setting a hard timeline for disbursing support funds.
• Innovative financial technologies, and a swift response from IFIs is needed to avert a liquidity crisis.
Session: Kabbage and IFC
Lesson 2: Asian SME lenders can provide an example:
• Preparation is key to adopting timely and effective actions.
• There is a need for adequate consumer-oriented responses.
• Lenders must quickly comply with fast-evolving regulations.
Session: Standard Chartered & Simple Credit
Lesson 3: Leverage innovation by establishing learning networks:
• Alibaba has successfully activated its digital business ecosystem.
• Ant Financial has swiftly designed and implemented a three-stage action plan.
• Importance of public-private partnerships.
• Every 1% increase in digital lending helps reduce the negative impact of COVID on the real economy by 2.57%. (according to analysis by Peking University Digital Finance Research Center).
Session: Alibaba and Ant Financial
Lesson 4: The crisis can be a catalyst for transformation in SME finance:
• Some lenders have moved the entire credit journey online.
• Think beyond loans and liquidity: focusing on capacity-building efforts.
• Different degrees of digital preparedness across the world.
• Credit risk assessment: drawing a clear distinction between chronic and COVID-19-related issues.
Session: DBS Singapore & FNB
Lesson 5: Credit guarantee schemes can play a vital role:
• Credit guarantee institutions (CGI) are powerful countercyclical instruments with deep experience in crisis management.
• Regulatory reform is needed to make CGIs more effective, e.g. relaxing state aid rules.
• CGIs themselves need to design innovative policies e.g. bond market intervention.
Example: KODIT
Note: This article will be updated on a regular basis.
About the Author
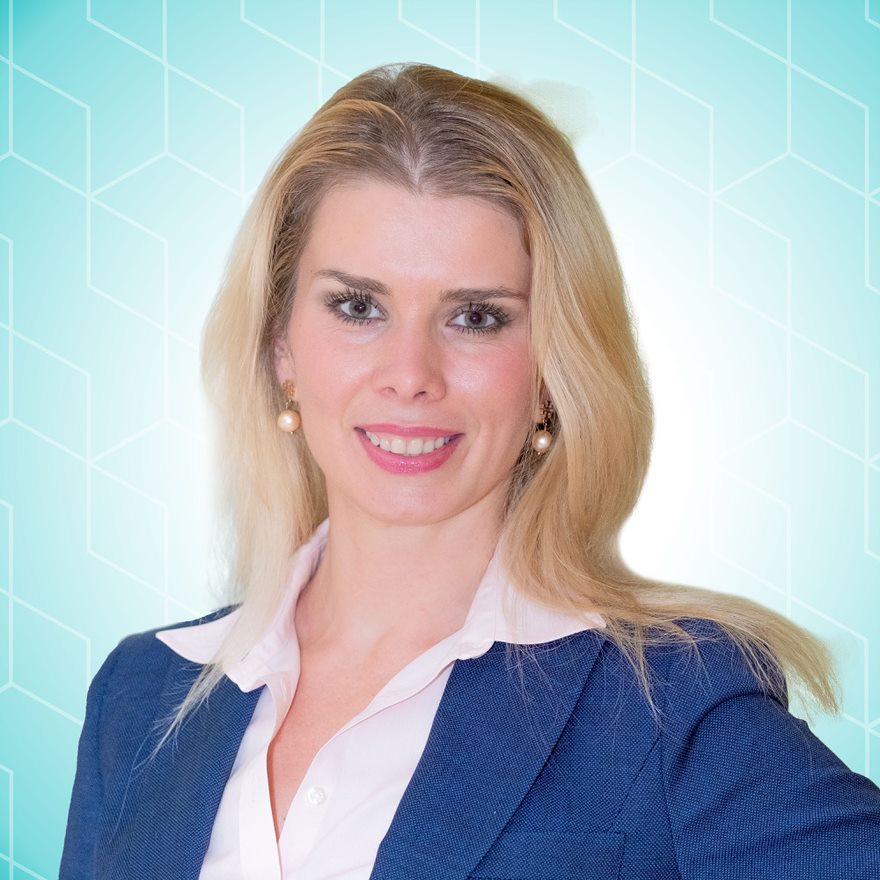 Khrystyna Kushnir works on knowledge management at the SME Finance Forum. She has over ten years of work experience in private enterprise and financial sector development. Before joining the Forum, Khrystyna worked as an operations analyst at the Development Economics of the World Bank Group. Prior to working for the Group, she was a Research Assistant for Central and Eastern Europe at the Heritage Foundation. Kushnir holds MA in International Economic Relations from the American University and is a Fulbright scholar.
Khrystyna Kushnir works on knowledge management at the SME Finance Forum. She has over ten years of work experience in private enterprise and financial sector development. Before joining the Forum, Khrystyna worked as an operations analyst at the Development Economics of the World Bank Group. Prior to working for the Group, she was a Research Assistant for Central and Eastern Europe at the Heritage Foundation. Kushnir holds MA in International Economic Relations from the American University and is a Fulbright scholar.